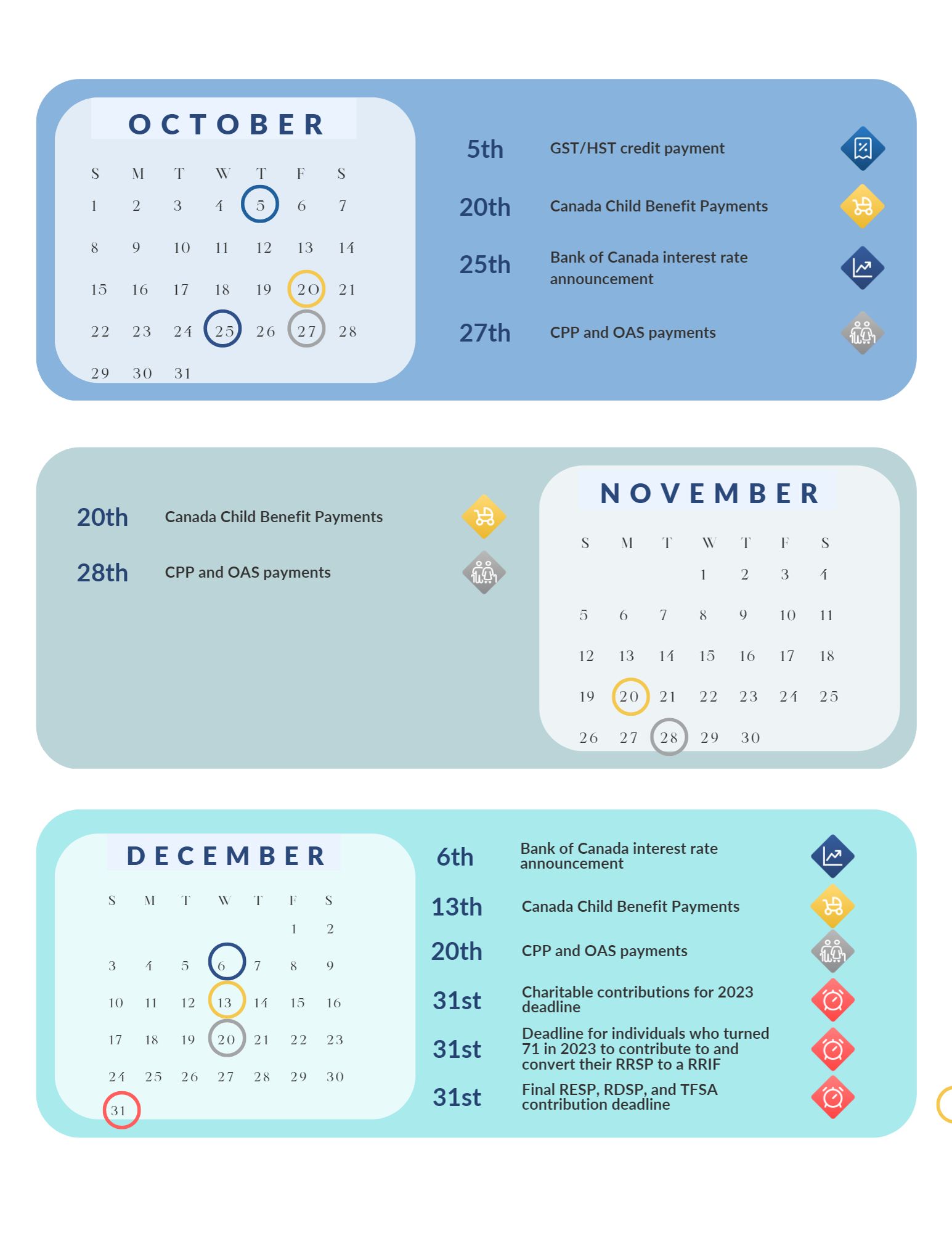
The end of 2022 is quickly approaching – which means it’s time to get your paperwork in order so you’re ready when it comes time to file your taxes!
In this article, we’ve covered four different major types of 2022 personal tax tips:
Investment Considerations
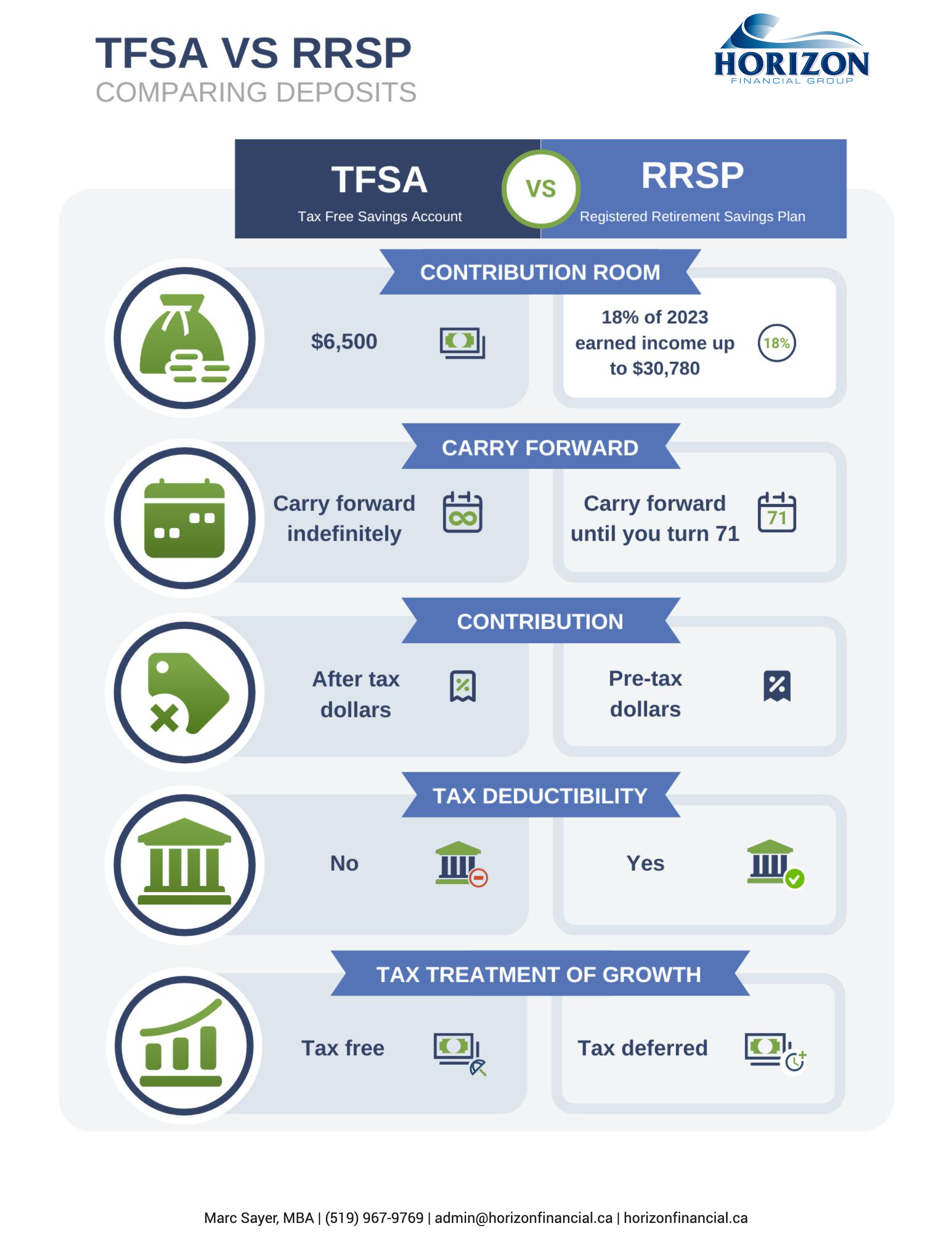
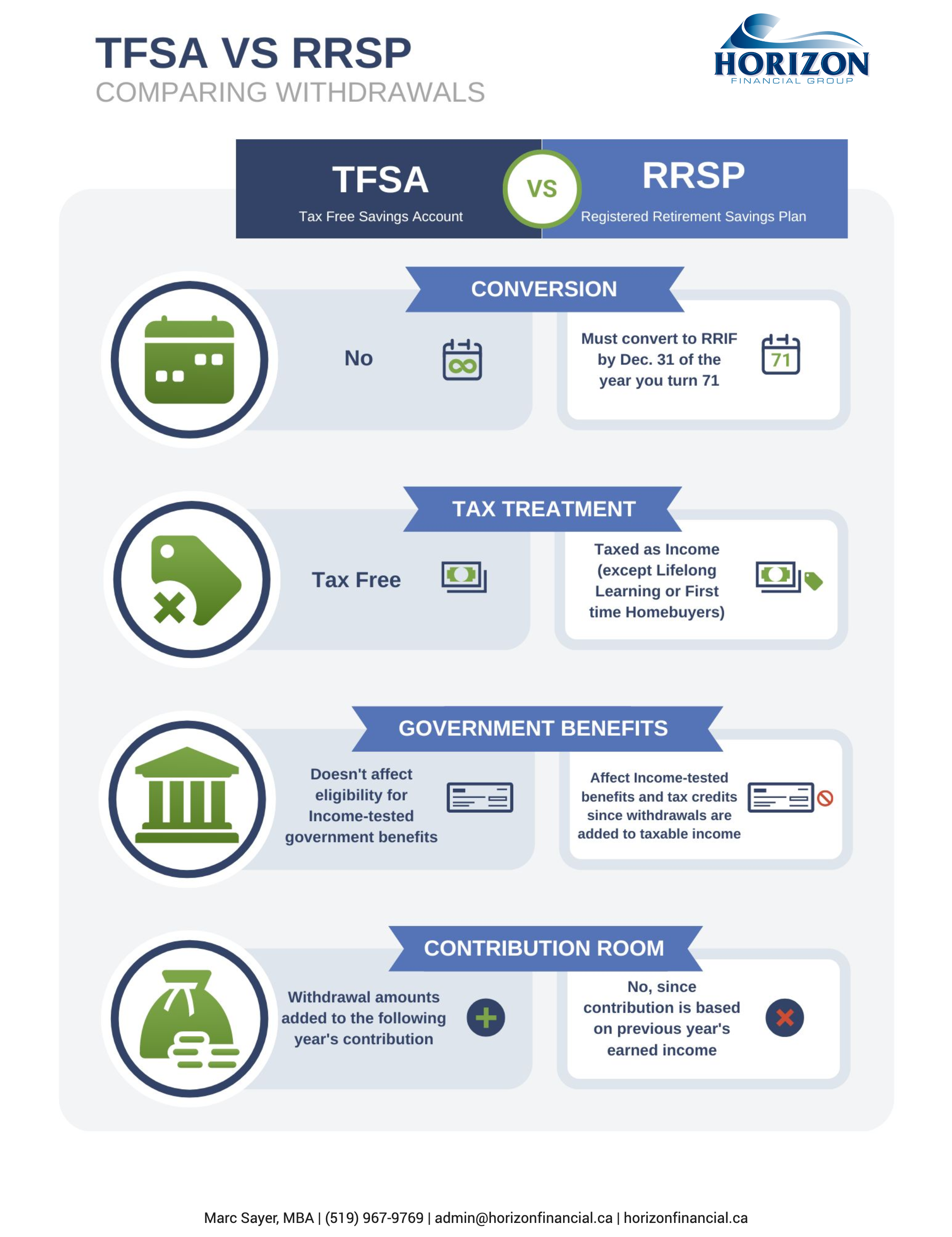
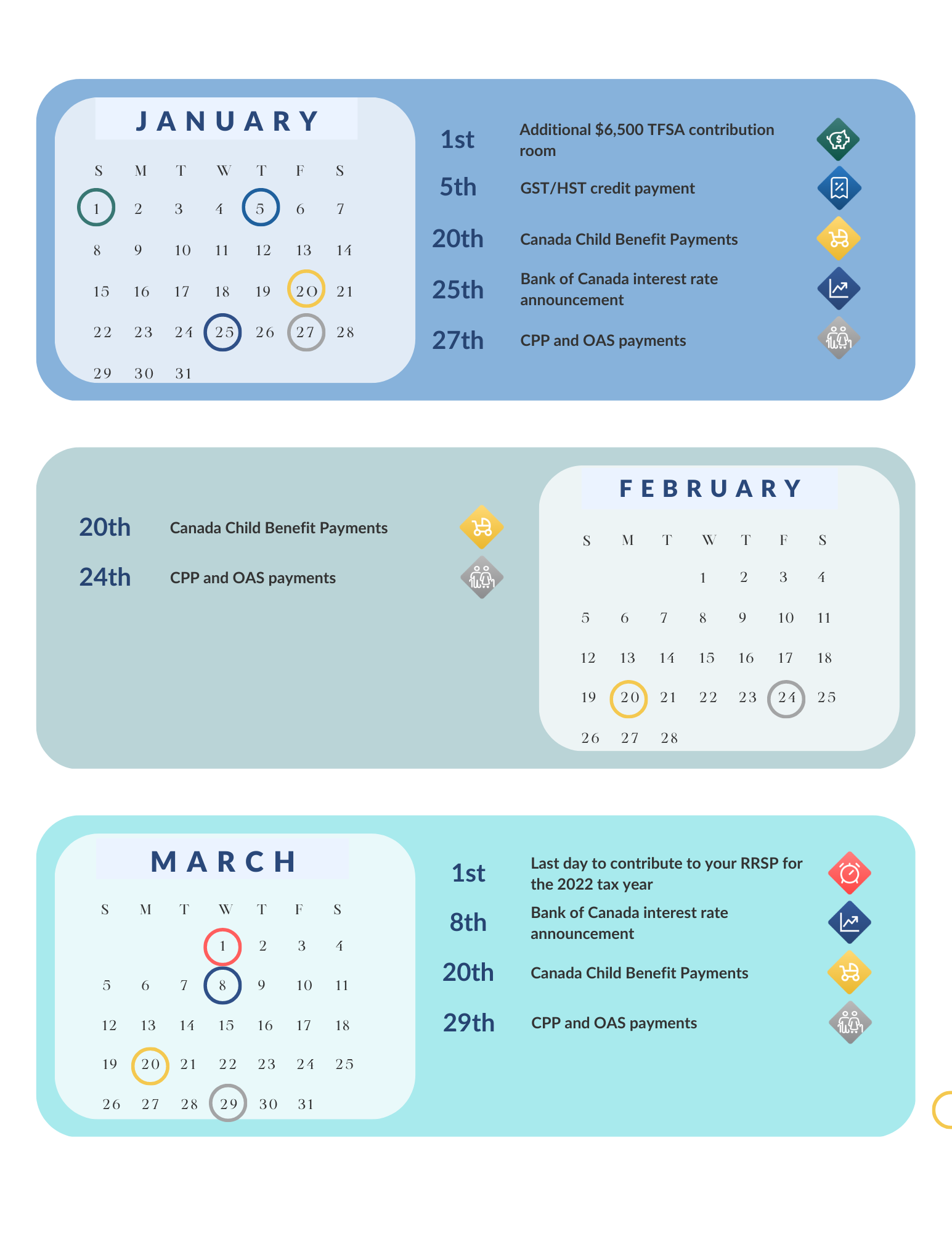
Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA)-You can contribute up to a maximum of $6000 for 2022. You can carry forward unused contribution room indefinitely. The maximum amount you’re allowed to make in TFSA contributions is $81,500 (including 2022).
Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP)- Contribute to your RRSP or a spousal RRSP. Remember that you can deduct contributions made within the first sixty days of the following calendar year from your 2022 income. You also have the option of carrying forward deductions. Consider the best mix of investments for your RRSP: hold growth investments outside the plan (to benefit from lower tax rates on capital gains and eligible dividends), and hold interest-generating investments inside. We can help if you need advice on how to make the most of your RRSP.
Do you expect to have any capital losses? If you have capital losses, sell securities with accrued losses before year end to offset capital gains realized in the current or previous three years. You must first deduct them against your capital gains in the current year. You can carry back any excess capital losses for up to three years or forward indefinitely.
Interest Deductibility – If possible, repay the debt that has non-deductible interest before other debt (or debt that has interest qualifying for a non-refundable credit, i.e. interest on student loans). Borrow for investment or business purposes and use cash for personal purchases. You can still deduct interest on investment loans if you sell an investment at a loss and reinvest the proceeds from the sale in a new investment.
Individuals
The following list may seem like a lot, but it’s unlikely every single tip will apply to you. It’s essential to make sure you aren’t paying taxes unnecessarily.
COVID-19 federal benefits – If you repay any COVID-19 benefit amounts before 2023, you can deduct from your income the repayment amount in the year in which the benefit amount was received instead of the year it was repaid. (You can also split the deduction between the two years.)
Income Timing – If your marginal personal tax rate is lower in 2023 than in 2022, defer the receipt of certain employment income; if your marginal personal tax rate is higher in 2023 than in 2022, accelerate.
Worked at home in 2022?-You may be able to deduct an income tax deduction for home office expenses. The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) has extended the availability of the simplified method—claiming a flat rate of $2 per day working at home due to the COVID-19 pandemic—to 2022. Consider what’s more advantageous for you to claim: the simplified or traditional method.
Medical expenses – If you have eligible medical expenses that weren’t paid for by either a provincial or private plan, you can claim them on your tax return. You can even deduct premiums you pay for private coverage! Either spouse can claim qualified medical expenses for themselves and their dependent children in a 12-month period, but it’s generally better for the spouse with the lower income to do so.
Charitable donations – Tax credits for donations are two-tiered, with a more considerable credit available for donations over $200. You and your spouse can pool your donation receipts and carry donations forward donations for up to five years. If you donate items like stocks or mutual funds directly to a charity, you will be eligible for a tax receipt for the fair market value, and the capital gains tax does not apply.
Moving expenses – If you’ve moved to be closer to school or a place of work, you may be able to deduct moving expenses against eligible income. You must have moved a minimum of 40 km.
Families
Childcare Expenses – If you paid someone to take care of your child so you or your spouse could attend school or work, then you can deduct those expenses. A variety of childcare options qualify for this deduction, including boarding school, camp, daycare, and even paying a relative over 18 for babysitting. Be sure to get all your receipts and have the spouse with the lower net income claim the childcare expenses. In addition, some provinces offer additional childcare tax credits on top of the federal ones.
Caregiver – If you are a caregiver, claim the available federal and provincial/territorial tax credits.
Children’s fitness, arts and wellness tax credits – If your child is enrolled in an eligible fitness or arts program, you may claim a provincial or territorial tax credit for fitness and arts programs.
Estate planning arrangements – Review your estate plan annually to ensure it reflects the current tax rules. Review your will to ensure that it will form a valid will. Consider strategies for minimizing probate fees.
Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) – can be a great way to save for a child’s future education. The Canadian Education Savings Grant (CESG) is only available on the first $2,500 of contributions you make each year per child (to a maximum of $500, with a lifetime maximum of $7,200.) If you have any unused CESG amounts for the current year, you can carry them forward. If the recipient of the RESP is now 16 or 17, they can only receive the CESG if a) at least $2,000 has already been contributed to the RESP and b) a minimum contribution of $100 was made to the RESP in any of the four previous years.
Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP) – If you have an RDSP open for yourself or an eligible family member, you may be able to get both the Canada Disability Savings Grant (CDSG) and the Canada Disability Savings Bond (CDSB) paid into the RDSP. The CDSB is based on the beneficiary’s adjusted family net income and does not require any contributions to be made. The CDSG is based on both the beneficiary’s family net income and contribution amounts. In addition, up to 10 years of unused grants and bond entitlements can be carried forward.
Retirees
Registered Retirement Income Fund (RRIF) – Turning 71 this year? If so, you are required to end your RRSP by December 31. You have several choices on what to do with your RRSP, including transferring your RRSP to a registered retirement income fund (RRIF), cashing out your RSSP, or purchasing an annuity. Talk to us about the tax implications of each of these choices!
Pension Income- Are you 65 or older and receiving pension income? If your pension income is eligible, you can deduct a federal tax credit equal to 15% on the first $2,000 of pension income received – plus any provincial tax credits! Don’t currently have any pension income? You may want to think about withdrawing $2,000 from an RRIF each year or using RRSP funds to purchase an annuity that pays at least $2,000 per year.
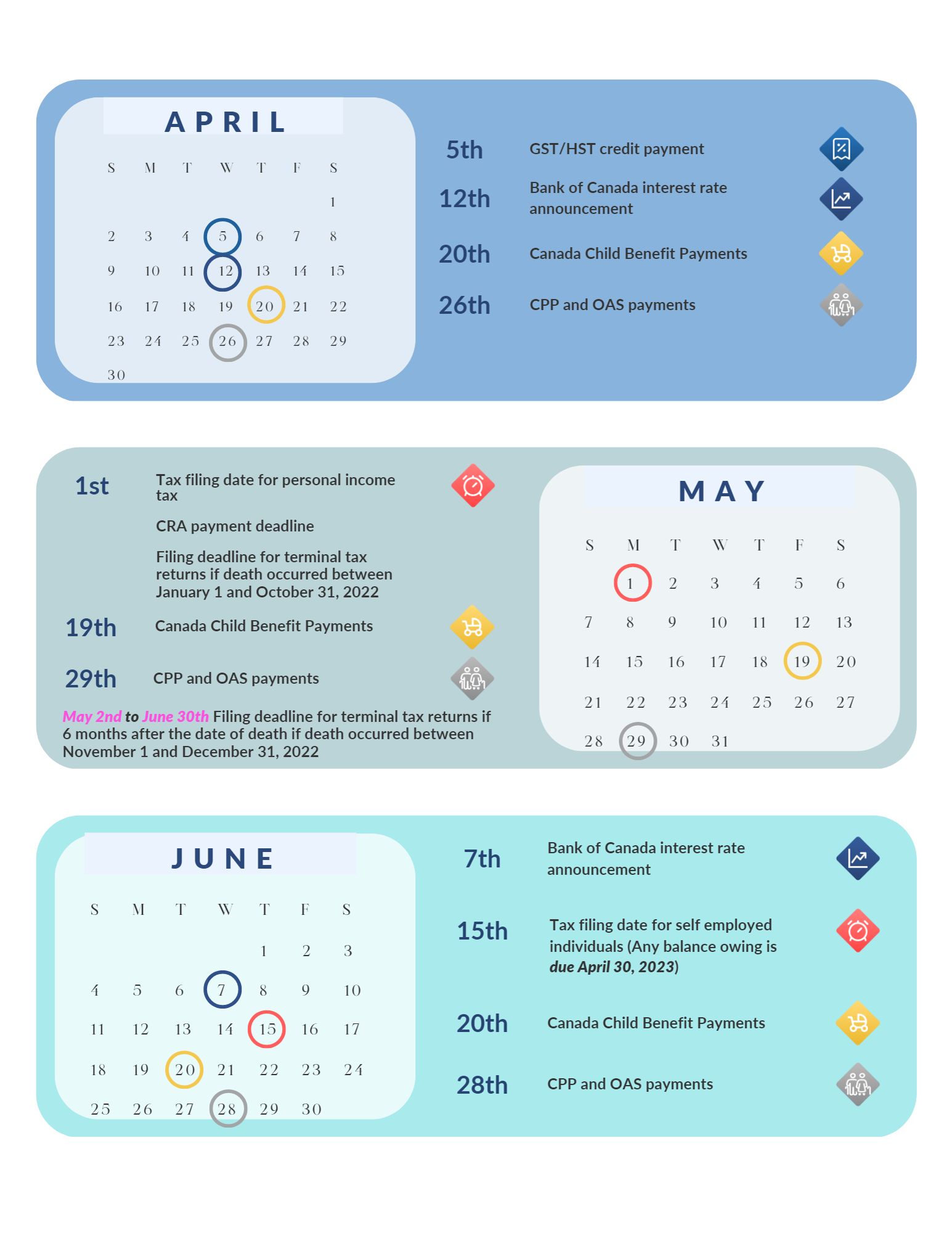
Canada Pension Plan (CPP) – If you’ve reached the age of 60, you may be considering applying for CPP. Keep in mind that if you do this, the monthly amount you’ll receive will be smaller. Also, you don’t have to have retired to be able to apply for CPP. Talk to us; we can help you figure out what makes the most sense.
Old Age Security – If you’re 65 or older, ensure you’re enrolled for Old Age Security (OAS) benefits. Retroactive OAS payments are only available for up to 11 months plus the month you apply for your OAS benefits. If you’re running into OAS “clawback” issues, consider ways to split or reduce other sources of income to avoid this.
Estate planning arrangements – Review your estate plan annually to ensure that it reflects the current tax rules. Consider strategies for minimizing probate fees. If you’re over 64 and living in a high probate province, consider setting up an inter vivos trust as part of your estate plan.
Students
Education, tuition, and textbook tax credits – If you’re attending post-secondary school, claim these credits where available.
Canada training credit – If you’re between 25 to 65 and enrolled in an eligible educational institution, you can claim a federal tax credit of $250 for 2021. You can claim tuition paid on your taxes, carry the amount forward, or transfer an unused tuition amount to a spouse, parent, or grandparent.
Need some additional guidance?
Reach out to us if you have any questions. We’re here to help.