Understanding Tax-Free Savings Accounts (TFSAs)
A Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA) is an investment vehicle available to Canadian residents. It offers numerous benefits, including tax-free growth of your investments and tax-free withdrawals. Before you decide to open a TFSA, it’s essential to understand the eligibility requirements, contribution limits, eligible investments, and withdrawal rules.
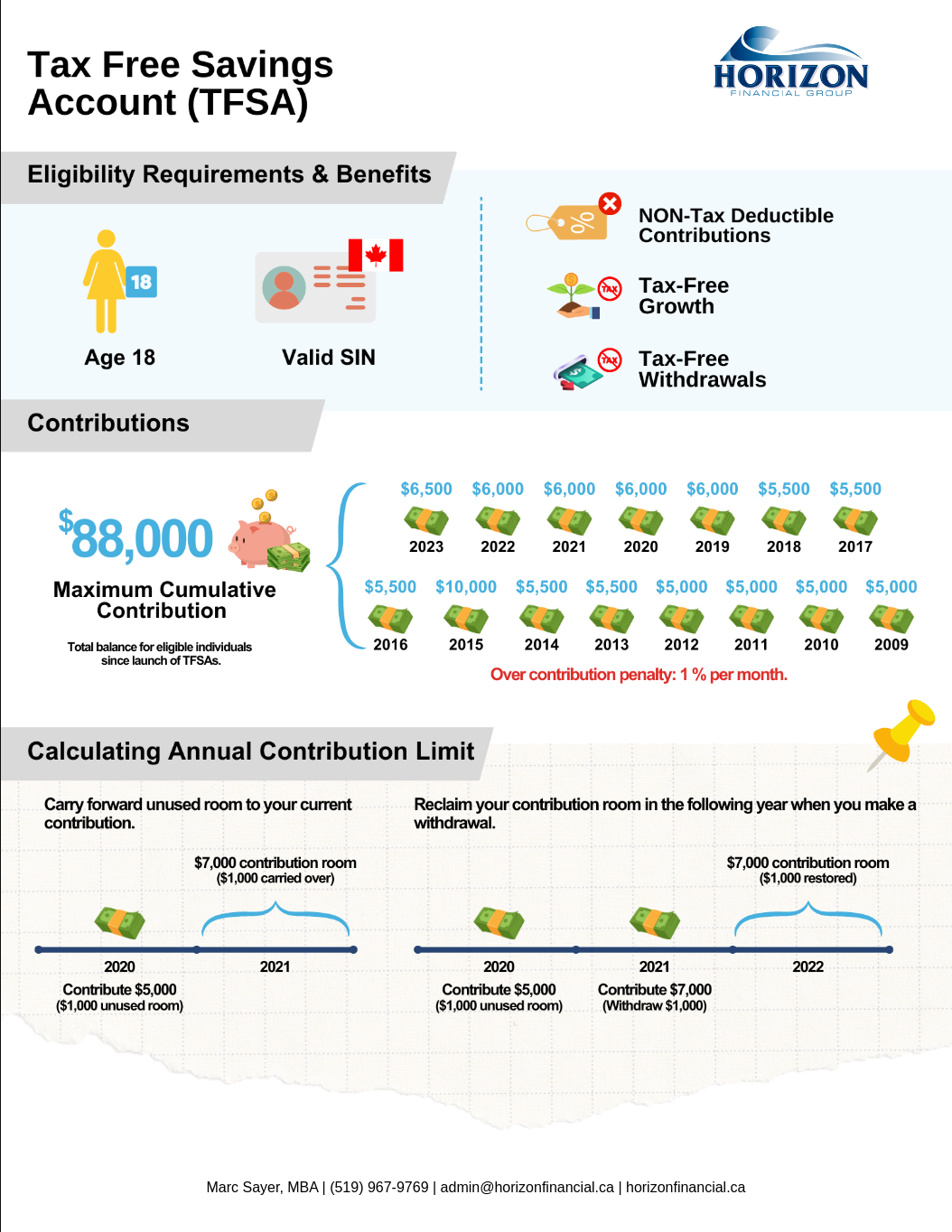
Eligibility Requirements
To open a TFSA, you must be a resident of Canada with a valid Social Insurance Number (SIN) and be at least 18 years old. However, in some provinces and territories, the legal age to enter a contract (which includes opening a TFSA) is 19. The TFSA contribution room for the year an individual turns 18 is carried over to the following year if the individual resides in a jurisdiction where the legal age is 19.
Benefits
One of the primary benefits of a TFSA is that it allows your investments to grow tax-free. Any income you earn from your investments within the TFSA is not taxed, even upon withdrawal. This includes interest, dividends, and capital gains.
Additionally, you can withdraw any amount from your TFSA at any time, and the withdrawals are tax-free. It’s important to note that withdrawing funds from your TFSA does not reduce the total amount of contributions you have made for the year. The amount withdrawn in a year will be added back to your TFSA contribution room at the beginning of the following year.
Contribution Limit
The annual TFSA dollar limit has varied over the years. From 2009 to 2012, it was $5,000; in 2013 and 2014, it was $5,500; in 2015, it increased to $10,000; from 2016 to 2018, it was $5,500; from 2019 to 2022, it was $6,000, and in 2023, it is $6,500. This annual limit will be indexed to inflation and rounded to the nearest $500.
The maximum amount you can contribute to a TFSA is determined by your TFSA contribution room. This room is the sum of the TFSA dollar limit of the current year, any unused TFSA contribution room from previous years, and any withdrawals made from the TFSA in the previous year.
Let’s look at two examples to better understand this:
Example #1: Carry Forward Unused Room to Your Current Contribution
In 2020, the annual TFSA contribution limit is $6,000. If you only contribute $5,000, you would have $1,000 of unused room. This unused room gets carried over to the next year. So, in 2021, the annual contribution room is $6,000, but because of the unused room from 2020, you actually have a total contribution room of $7,000 ($6,000 for 2021 + $1,000 carried over from 2020).
Example #2: Reclaim Your Contribution Room in the Following Year When You Make a Withdrawal
In 2021, you have $7,000 in contribution room and decide to contribute the full amount. However, you also decide to make a withdrawal of $1,000 in 2021. In 2022, the annual contribution limit is $6,000, but because of the withdrawal made in 2021, you actually have a total contribution room of $7,000 ($6,000 for 2022 + $1,000 withdrawn in 2021).
Please note that if you exceed your available TFSA contribution room at any time in the year, you will have to pay a tax equal to 1% of the highest excess TFSA amount in the month, for each month that the excess amount stays in your account.
Eligible Investments
The types of investments that are permitted in a TFSA are generally the same as those allowed in a Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP). These include cash, segregated funds, mutual funds, securities listed on a designated stock exchange, guaranteed investment certificates, and bonds.
Withdrawals
As mentioned earlier, you can generally withdraw any amount from the TFSA at any time, depending on the type of investment held in your TFSA. However, if you decide to replace or re-contribute all or a part of your withdrawals into your TFSA in the same year, you can only do so if you have available TFSA contribution room.
For example, if in 2023 you withdraw $1,000 from your TFSA and later in the same year decide to re-contribute that amount, you can only do so if your contribution room for 2023 allows for it. If it doesn’t and you re-contribute the $1,000 anyway, you will be considered to have over-contributed to your TFSA in that year. This will result in a tax equal to 1% of the highest excess TFSA amount in the month, for each month that the excess amount stays in your account
Beneficiary
When establishing a Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA), you are given the choice to designate a beneficiary. This person will be the recipient of the investments within your TFSA in the event of your death. The assets inherited by the beneficiary are not considered income, and as such, are received tax-free. It’s important to note, though, that while the inherited amount is tax-free, the beneficiary will be responsible for any tax on earnings that the TFSA generates after the original account holder’s death.
Start Planning for Your Future Today!



