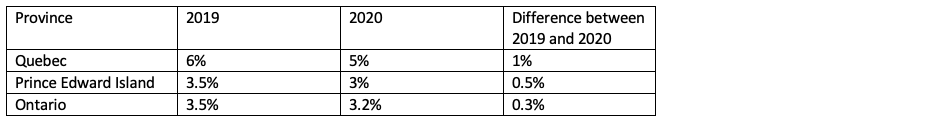
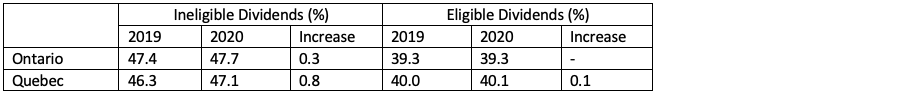
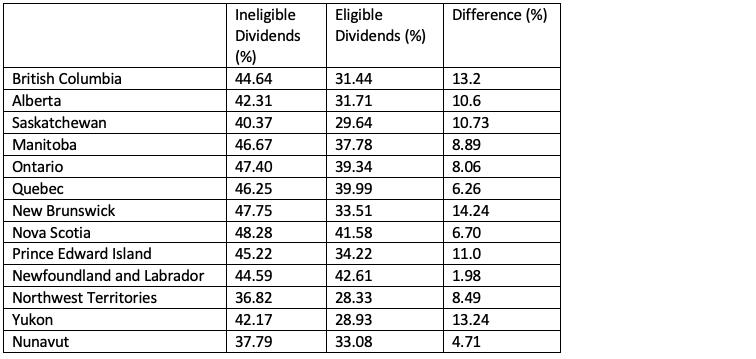
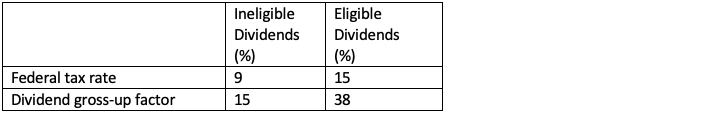
Therefore, a small business deduction in 2019 is worth more than in 2020 for these provinces.
Should you repay any shareholder loans?
Loaning funds from your corporation at a low or zero interest rate means that you are considered to have benefited from a taxable benefit at the CRA’s 2% interest rate, less actual interest that you pay during the year or thirty days after it. You need to include the loan in your income tax return, unless it is repaid within one year after the end of your corporation’s taxation year.
For example, if your company has a December 31st year-end and it loaned you funds on November 1, 2019, you must repay the loan by December 31, 2020, otherwise you will need to include the loan as taxable income in your 2019 personal tax return.
Passive investment income
If your corporation has a December year- end, then 2019 will be the first taxation year that the new passive investment income rules may apply to your company.
New measures were introduced in the 2018 federal budget relating to private businesses which also earn passive investment income in a corporation that also operates an active business.
There are two key parts to this, as follows:
-
Limiting access to dividend refunds. Essentially, a private company will be required to pay ineligible dividends in order to receive dividend refunds on some taxes which, in the past, could have been refunded when an eligible dividend was paid.
-
Limiting the small business deduction. This means that, for the companies mentioned above, the small business deduction can be reduced at a rate of $5 for every $1 over between $50,000 and $150,000 of investment income, or eliminated if investment income exceeds $150,000. Please note that Ontario and New Brunswick have indicated that they will not follow the federal rules.
If your corporation earns both active business and passive investment income, you should contact us and your accountant directly to determine if there are any planning opportunities to minimize the impact of the new passive investment income rules.
Think about when to pay dividends and dividend type
When choosing to pay dividends in 2019 or 2020, you should consider the following:
-
Difference between the yearly tax rate
-
Impact of tax on split income
-
Impact of passive investment income rules
With the exception of 2 provinces, Quebec and Ontario, the combined top marginal tax rates will not be changing from 2019 to 2020 on a provincial level. Therefore, it will not make a difference if you choose to pay in 2019 or 2020.
Combined Marginal Tax Rate