2021 Personal Year-End Tax Tips
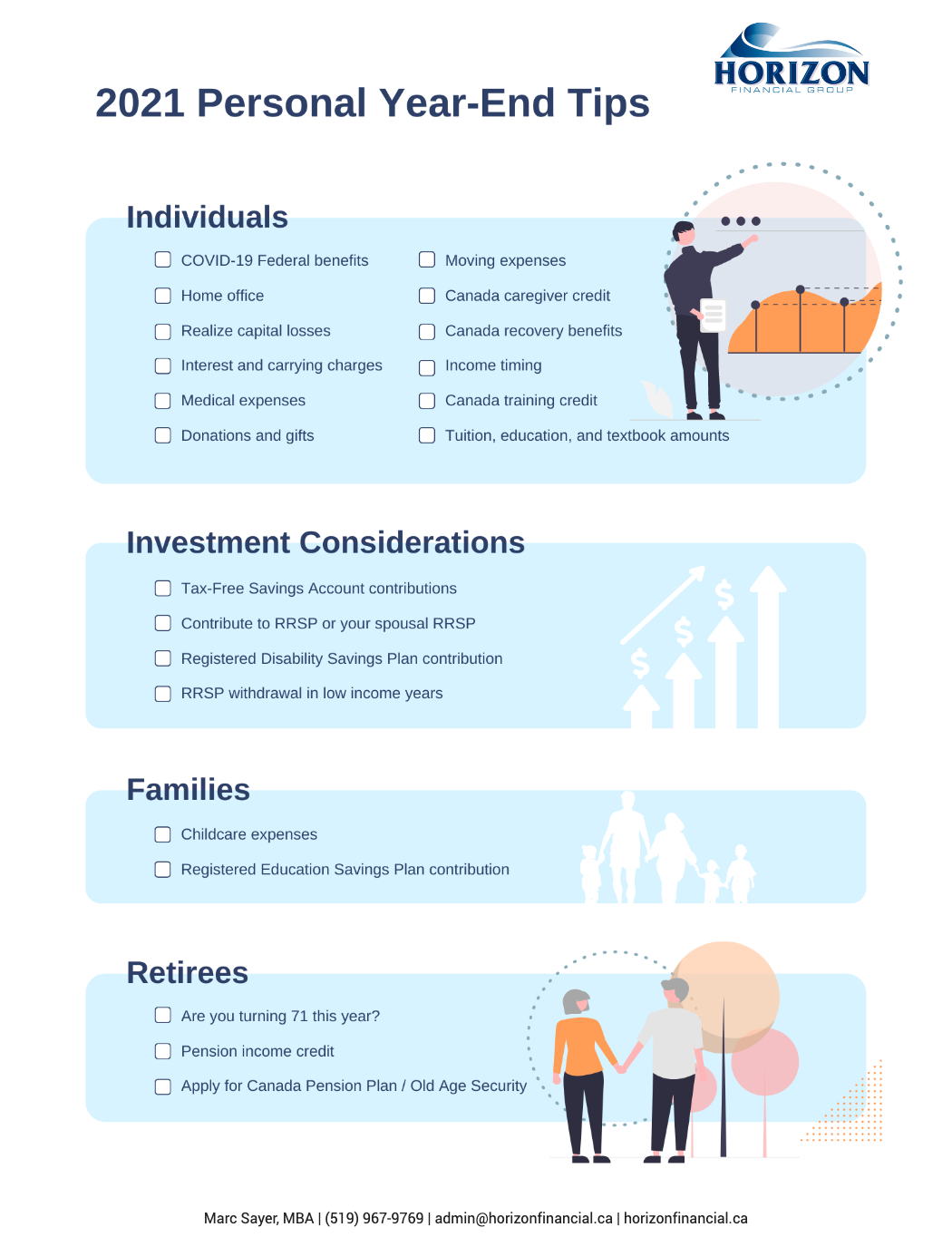
The end of 2021 is quickly approaching – which means it is time to get your finances in order, so you are ready when it comes time to file your taxes.
In this article, we cover four types of 2021 personal tax tips:
-
Individuals
-
Investment Considerations
-
Families
-
Retirees
Individuals
It is essential to make sure you are not paying taxes unnecessarily.
These are the main COVID-19 benefits for individuals:
-
You can apply for the Canada Recovery Benefit if you are not eligible for EI and can not work due to COVID-19 or have had your income reduced due to COVID-19. This benefit ended as of October 23, 2021, but you can still claim the last eligible period until December 22, 2021.
-
You can apply for the Canada Recovery Sickness Benefit if you are sick or need to self-isolate due to COVID-19. This benefit is scheduled to end on November 21, 2021, but legislation has been proposed to extend it to next May.
-
You can apply for the Canada Recovery Caregiving Benefit if you can not work because you need to supervise a child or other dependent family member because they are ill with COVID-19 or their usual school or other facility is closed. This benefit is scheduled to end on November 21, 2021, but legislation has been proposed to extend this benefit to next May.
-
A new Canada Worker Lockdown Benefit provides $300 a week if you can not work due to a government-imposed lockdown (and are not receiving EI). This benefit is proposed, and legislation for this benefit has not been passed.
You must apply for these benefits no later than 60 days after the end of the claim period. You will receive a T4A from the CRA and must report any money received from these benefits as income on your 2021 tax return.
All Canada Recovery Benefits (CRB) are subject to a 10% withholding tax. If you earned over $38,000 in net income in 2021, you might be required to reimburse the government some or all of the CRB at tax time. You can use tax deductions such as RRSP contributions to avoid either additional tax on these recovery benefits or reduced benefits.
If you have to repay any COVID-19 benefits, you can deduct the repayment amount from your income in the year you received the benefit.
For 2020, the CRA introduced a simplified process for claiming a deduction for home office expenses for employees working from home due to COVID-19. An employee can either claim using a new temporary flat rate method or use the more traditional method for claiming home office expenses. We assume a similar approach will be allowed for 2021, so be sure to track all your home office expenses.
Do you expect to have any capital losses? If you have capital losses, you must first deduct them against any capital gains you had in the current year. After that, you can carry back any excess capital losses up to three years or forward indefinitely. Trades can take up to two days to settle, so be sure to sell any investments you want to claim a capital loss on by December 29 at the latest.
You can deduct any fees you pay to manage or administer your non‑registered investments. As well, you can usually deduct interest charges paid on borrowed money if you used the money to earn income from non‑registered investments or a business. If you have non-deductible interest, like a mortgage or car loan, talk to your tax advisor to see if you can restructure your investments to make the interest on these loans tax‑deductible.
If you have eligible medical expenses that were not paid for by either a provincial or private plan, you can claim these expenses against your taxes. You can even deduct premiums you pay for private coverage. Either spouse can claim qualified medical expenses for themselves and dependent children in a 12-month period. However, it is generally better for the spouse with a lower income to claim the expense because the credit is reduced by a percentage of net income. If the lower-income spouse does not have enough tax payable to offset the medical expense tax credit, it may be beneficial to move the expenses to the higher-income spouse.
Tax credits for donations are two-tiered, with a larger credit being available for donations over $200. You and your spouse can pool your donation receipts and carry donations forward for up to five years. If you donate items like stocks or mutual funds directly to a charity, you will be eligible for a tax receipt for the fair market value, and the capital gains tax does not apply.
If you have moved to be closer to school or a place of work, you may be able to deduct moving expenses against eligible income. You must have moved a minimum of 40 km.
If you care for a dependent relative with a mental or physical impairment, you may be able to claim a non-refundable tax credit.
Will your personal tax rate be lower in 2022 than it will be for 2021? If so and have the option, you may wish to defer receiving income to 2022. And if your tax rate will be higher in 2022 than for 2021, try to accelerate income and receive it before the end of 2021.
There are a few options available to you when it comes to tax tips if you are enrolled in school:
-
If you are between the ages of 25 to 65 and enrolled in an eligible educational institution, you can claim a federal tax credit of $250 for 2021.
-
You can claim tuition paid on your taxes, carry the amount forward, or transfer an unused tuition amount to a spouse, parent, or grandparent.
Investment Considerations
Depending on your circumstances, there are up to three different ways you can set aside money in registered accounts to save for the future:
-
Contribute to your Tax Free Savings Account (TFSA). You can contribute up to a maximum of $6000 for 2021. You can carry forward unused contribution room indefinitely. For instance, if you have never contributed to your TFSA, the cumulative total from 2009 to 2021 is $75,500.
-
Contribute to your RRSP or a spousal RRSP. Remember, you can deduct contributions made in the year or within the first sixty days of the following calendar year from your 2021 income. You also have the option of carrying forward deductions.
-
Suppose you have an RDSP open for yourself or an eligible family member. You may be able to have both the Canada Disability Savings Grant (CDSG) and the Canada Disability Savings Bond (CDSB) paid into the RDSP. The CDSB is based on the beneficiary’s adjusted family net income and does not require any contributions to be made. The CDSG is based on both the beneficiary’s family net income and contribution amounts. In addition, up to 10 years of unused grants and bond entitlements can be carried forward.
If you need extra money this year because your income was unusually low, you may want to consider making an RRSP withdrawal before the end of the year to boost your income. This is generally only a good idea if you are in the lowest tax bracket. Be aware that you will permanently lose that contribution room if you withdraw money from an RRSP. However, if you are concerned about whether making an RRSP withdrawal is a good strategy for you, we are happy to answer any questions you may have.
Families
If you paid someone to take care of your child so you or your spouse could attend school or work, then you can deduct these expenses. Various childcare expenses qualify for this deduction, including boarding school, camp, daycare, and even paying a relative over 18 for babysitting.
Be sure to get all your receipts and have the spouse with the lower net income claim the childcare expenses. Some provinces offer additional childcare tax credits on top of the federal ones.
A Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) can be a great way to save for a child’s future education. However, the Canadian Education Savings Grant is only available on the first $2,500 of contributions you make each year per child (to a maximum of $500, with a lifetime maximum of $7,200.).
If you have any unused CESG amounts for the current year, you can carry them forward. If the recipient of the RESP is now 16 or 17, they can only receive the CESG if:
a) at least $2,000 has already been contributed to the RESP and
b) a minimum contribution of $100 was made to the RESP in any of the four previous years.
Retirees
Are you turning 71 this year? If so, you are required to end your RRSP by December 31. You have several choices on what to do with your RRSP, including transferring your RRSP to a Registered Retirement Income Fund (RRIF), cashing out your RSSP, or purchasing an annuity. Talk to us about the tax implications of each of these choices.
65 or older and receiving pension income? If your pension income is eligible, you can deduct a federal tax credit equal to 15% on the first $2,000 of pension income received – plus any provincial tax credits.
Do you not currently have any pension income? Then, you may want to think about withdrawing $2,000 from an RRIF each year or using RRSP funds to purchase an annuity that pays at least $2,000 per year.
If you have reached the age of 60, you may be considering applying for the Canada Pension Plan. However, keep in mind that the monthly amount you will receive will be lower if you apply at 60 versus a later age. Keep in mind, you do not have to have retired to apply for CPP.
If you are 65 or older, ensure that you are enrolled for Old Age Security (OAS) benefits. Retroactive OAS payments are only available for up to 11 months plus the month you apply for your OAS benefits. If you are running into OAS “clawback” issues, consider ways to split or reduce other sources of income to avoid this clawback.
Need some additional guidance?
We hope you have enjoyed all of our tax tips. If you have questions or want help to make sure you use all the tax deductions you are eligible for, reach out to us and set up a time to talk.



-Marc-Sayer-mcRRGELp35qWo7yqd.png)





-Marc-Sayer-mcRRGELp35qWo7yqd.png)