Estate Planning for Business Owners
Estate Planning for Business Owners
What happens when the children grow up and they are no longer dependent on their parents? What happens to your other “baby”- the business? Estate planning for business owners deals with the personal and business assets. Business succession planning is different because it deals with your business assets only and can also take place while you’re alive. You need to have an estate plan regardless if you have a succession plan or not. Estate planning for business owners is typically more complicated because the estate plan needs to deal with:
-
Complex business and personal relationships
-
Bigger and more intricate estates
-
Tax issues
-
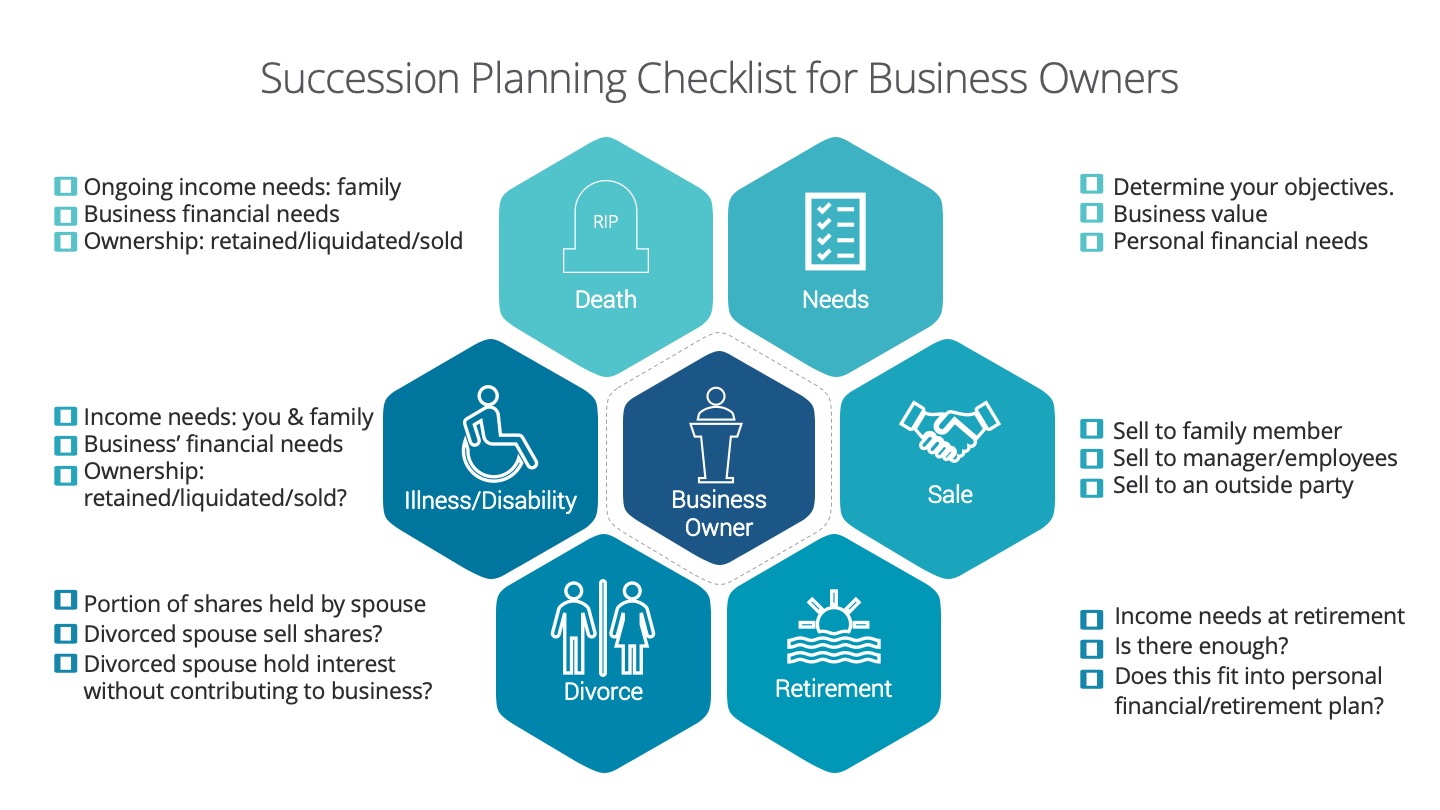
Business Succession
When putting an estate plan for a business owner together, one of the most difficult conversations is around fair or equal distribution of assets. What if one of the children are working in the business how do you treat them? Before you begin putting a plan in place, we always encourage open conversation and a family meeting between the parents and children to provide context behind decisions and therefore it minimizes the surprises and provides an opportunity for children to express their concerns.
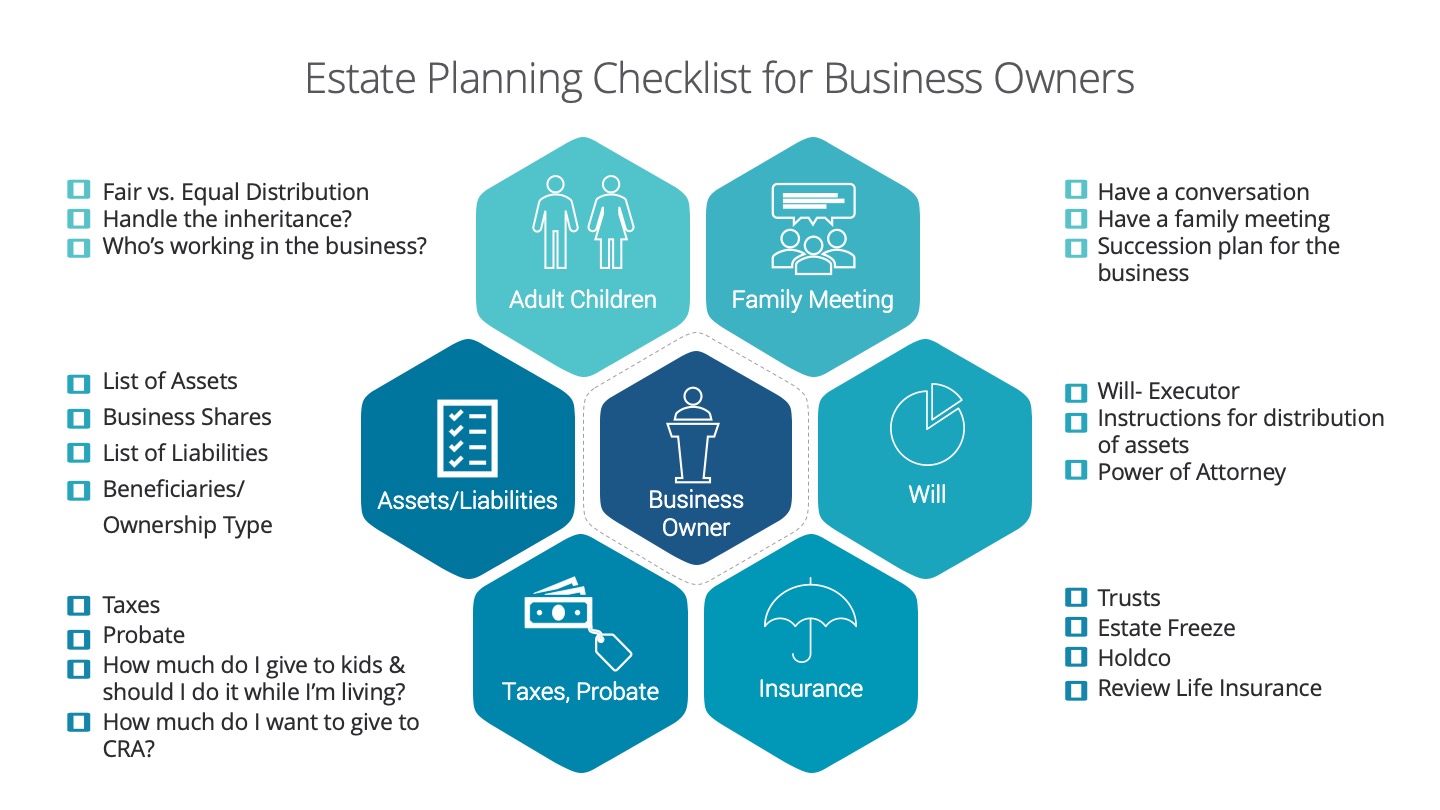
We’ve put together an infographic checklist that can help you get started on this. We know this can be a difficult conversation so we’re here to help and provide guidance.
Adult Children
-
Fair vs Equal (also known as Equitable vs Equal) – like what’s considered to be fair may not necessarily be equal. ex. Should the daughter that’s been working in the family business for 10 years receive the same shares as the son who hasn’t worked in the family business at all?
-
Are the adult children responsible enough to handle the inheritance? Or would they spend it all?
-
Who works in the family business? Is it all the kids or just one of them?
Family Meeting
-
Encourage open conversation with parents and kids so context can be provided behind the decisions, there are no surprises and allows the kids to express their interests and concerns.
-
Facilitate a family meeting with both generations, this will help promote ongoing family unity after death and decrease the chances of resentment later.
-
Start looking at considerations for a succession plan for the business. (This needs to be documented separately.)
Assets/Liabilities
-
What are your assets? Create a detailed list of your assets such as:
-
Home, Real Estate, Investments- Non registered, TFSA, RRSP, RDSP, RESP, Company Pension Plan, Insurance Policy, Property, Additional revenue sources, etc..
-
What about shares in your business? How does this need to be addressed?
-
What are your liabilities? Create a detailed list of your liabilities such as:
-
Mortgage, Loans (personal, student, car), Line of Credit, Credit card, Other loans (payday, store credit card, utility etc.)
-
Did you personally guarantee any business loans and how does this need to be addressed?
-
Understand your assets-the ownership type (joint, tenants in common, sole etc.), list who are the beneficiaries are for your assets
-
Understand your liabilities- are there any co-signors?
Make sure you have a will that:
-
Assigns an executor.
-
Provide specific instructions for distribution of all assets.
-
Consider a power of attorney for use when you’re incapacitated or otherwise unable to handle your affairs.
-
Always choose 2 qualified people for each position and communicate with them.
Taxes and Probate
-
How much are probate and taxes? (Income tax earned from Jan 1 to date of death + Taxes on Non Registered Assets + Taxes on Registered Assets, Taxes on Business Shares)
-
Are there any outstanding debts to be paid?
-
You’ve worked your whole life- how much of your hard earned money do you want to give to CRA?
-
How much money do you want to to give to your kids while you’re living?
Consider the following:
-
The use of trusts.
-
The use of an estate freeze if you wish to gift while you’re living.
-
The use of a holdco for effective tax planning.
-
Once you determine the amount of taxes, probate, debt, final expenses and gifts required, review your life insurance coverage to see if it meets your needs or if there’s a shortfall.
Execution:It’s good to go through this but you need to do this. Besides doing it yourself, here’s a list of the individuals that can help:
-
Financial Planner/Advisor (CFP)
-
Estate Planning Specialist
-
Insurance Specialist
-
Lawyer
-
Accountant/Tax Specialist
-
Chartered Life Underwriter (CLU)
-
Certified Executor Advisor (CEA)
Next steps…
-
Contact us about helping you get your estate planning in order so you can gain peace of mind that your family is taken care of.