Personal Life Insurance Planning
Personal Life Insurance Planning
When thinking about life insurance, one of the most important steps is figuring out how much coverage you need. Everyone’s situation is unique, but a helpful starting point is understanding your coverage options and thinking about the areas of your life that need protection.
Understanding the Different Types of Life Insurance
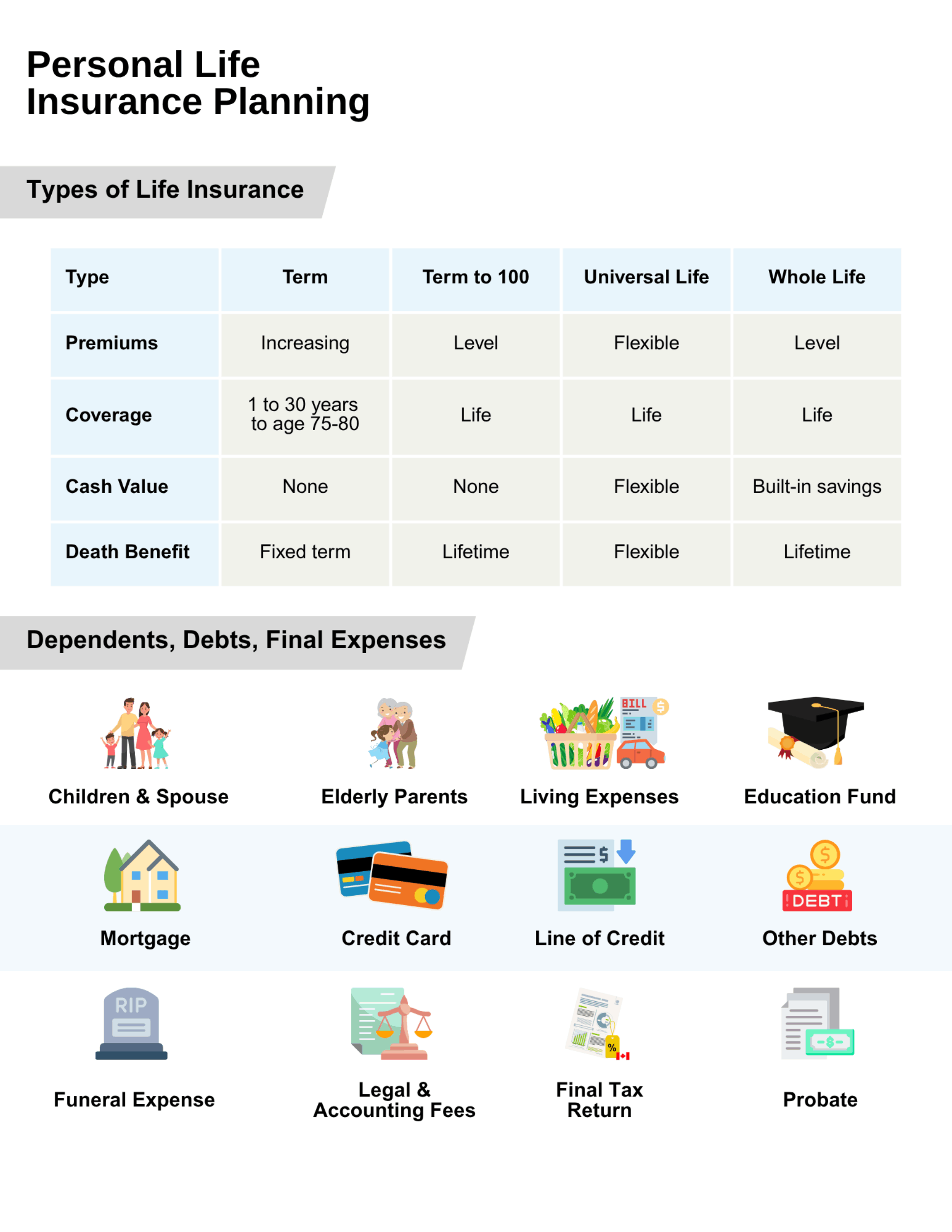
There are four main types of life insurance: Term, Term to 100, Universal Life, and Whole Life. Here’s how they compare:
Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific number of years—typically 10, 20, or 30 years. It offers fixed premiums for the length of the term, and if renewed, premiums will increase based on your age. This type of insurance provides a fixed death benefit during the coverage period and does not build any cash value.
Ideal For: Families with children, people with mortgages or temporary debts
Death Benefit – Common Uses: Income replacement, mortgage protection, child education
Term to 100
Term to 100 offers lifetime coverage with level premiums that are payable until age 100. It is a cost-effective way to get permanent insurance, as it does not accumulate cash value. The policy provides a death benefit as long as premiums are paid.
Ideal For: Those wanting lifetime coverage without investment features
Death Benefit – Common Uses: Final expenses, estate taxes, leaving a small legacy
Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance is a flexible form of permanent insurance that includes both a death benefit and a tax-advantaged investment component. You can adjust your premium payments and death benefit within certain limits. The policy’s cash value depends on how much you contribute and the performance of the chosen investments. Funds can be used for investment growth, savings, personal use, and retirement planning.
Ideal For: People who want long-term coverage with savings but require flexibility
Death Benefit Uses: Advanced estate planning, long-term wealth transfer
Cash Value Uses: Emergency funding, retirement planning, education funding, large purchases
Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance provides permanent coverage with level premiums and a death benefit. It also builds cash value over time, which you can borrow against, withdraw from, or use to help pay premiums. The cash value may be accessed for emergencies, supplementing retirement income, large purchases, or other long-term needs.
Ideal For: People who want long-term coverage with savings
Death Benefit Uses: Estate planning, legacy, long-term protection
Cash Value Uses: Emergency funding, retirement planning, education funding, large purchases
The need for life insurance
Once you understand your options, the next step is identifying the purpose of the insurance in your life. Most needs fall into three main categories:
Dependents
Whether it’s young children, a spouse, or even elderly parents, many families have one or more people who depend on their income. In these cases, life insurance plays an important role in maintaining the household’s financial stability. It can help pay for groceries, monthly bills, childcare, tuition, or even a car replacement down the road. Think of it as a financial bridge that helps your family maintain their standard of living while they adjust to life without your income.
Debts
Do you have a mortgage? A home equity line of credit? Maybe a personal loan or credit cards with balances that carry over month to month? If something unexpected were to happen, life insurance can ensure those debts don’t fall on your family’s shoulders. A properly structured policy can provide enough to pay off major liabilities, giving your family financial breathing room and the security of keeping their home or lifestyle intact.
Final Expenses
End-of-life costs often catch families off guard. Between funeral expenses, legal and accounting fees, final tax returns, and probate costs, the total can easily reach into the tens of thousands. A life insurance policy can provide immediate funds to help cover these costs without dipping into savings or relying on credit. For many retirees or aging parents, this is one of the biggest reasons to have a policy—even a small one.
Bringing It All Together
Choosing the right life insurance depends on your personal and family goals. Whether you’re protecting your home, your loved ones’ lifestyle, or planning for future expenses, there’s a policy that fits your needs.
If you’re not sure where to start, a good first step is reviewing your current debts, thinking through future costs, and considering who depends on you.
We’re here to help you choose the right coverage—get in touch.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, legal, or tax advice. Always consult a qualified professional regarding your specific situation. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on this content.



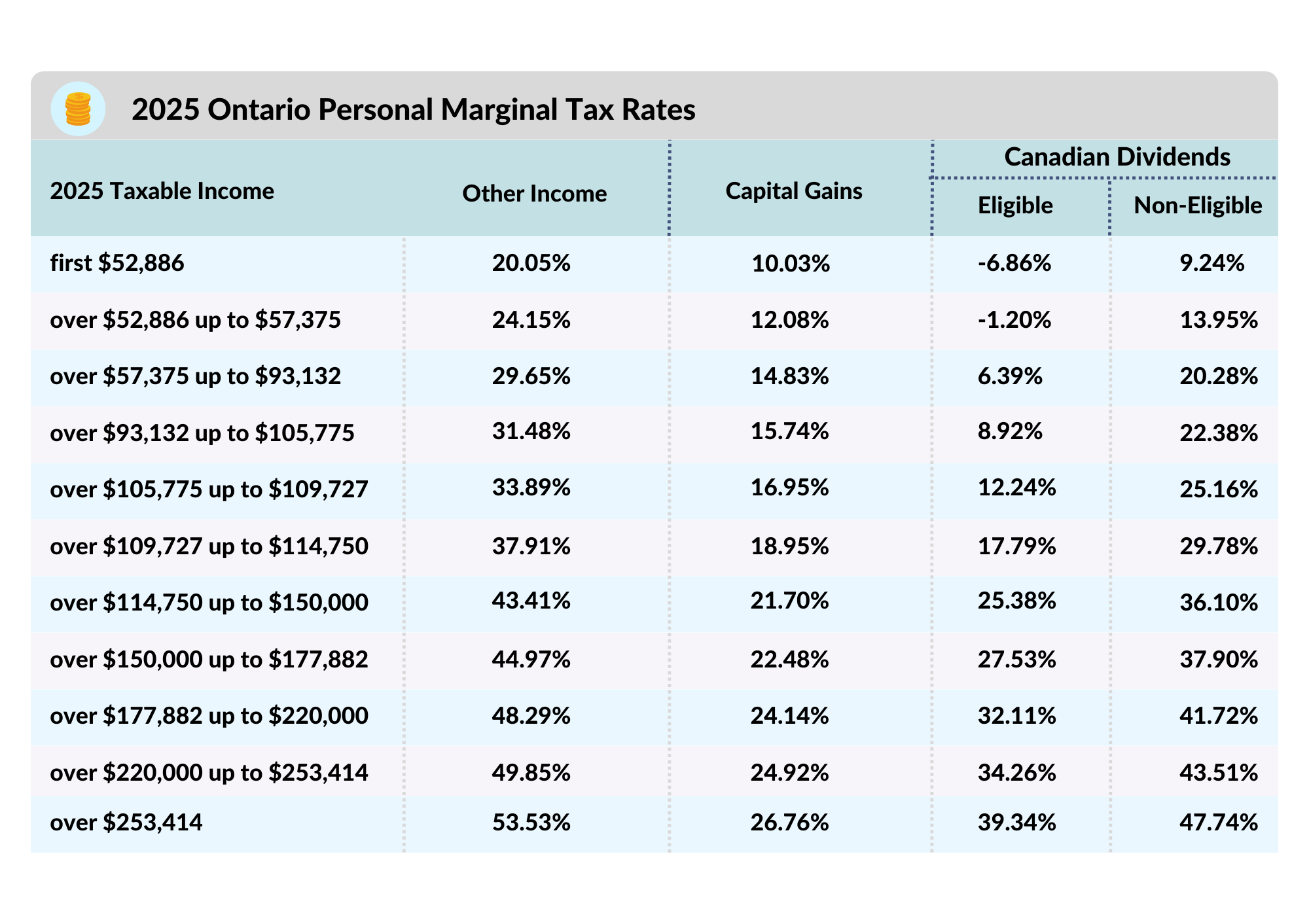
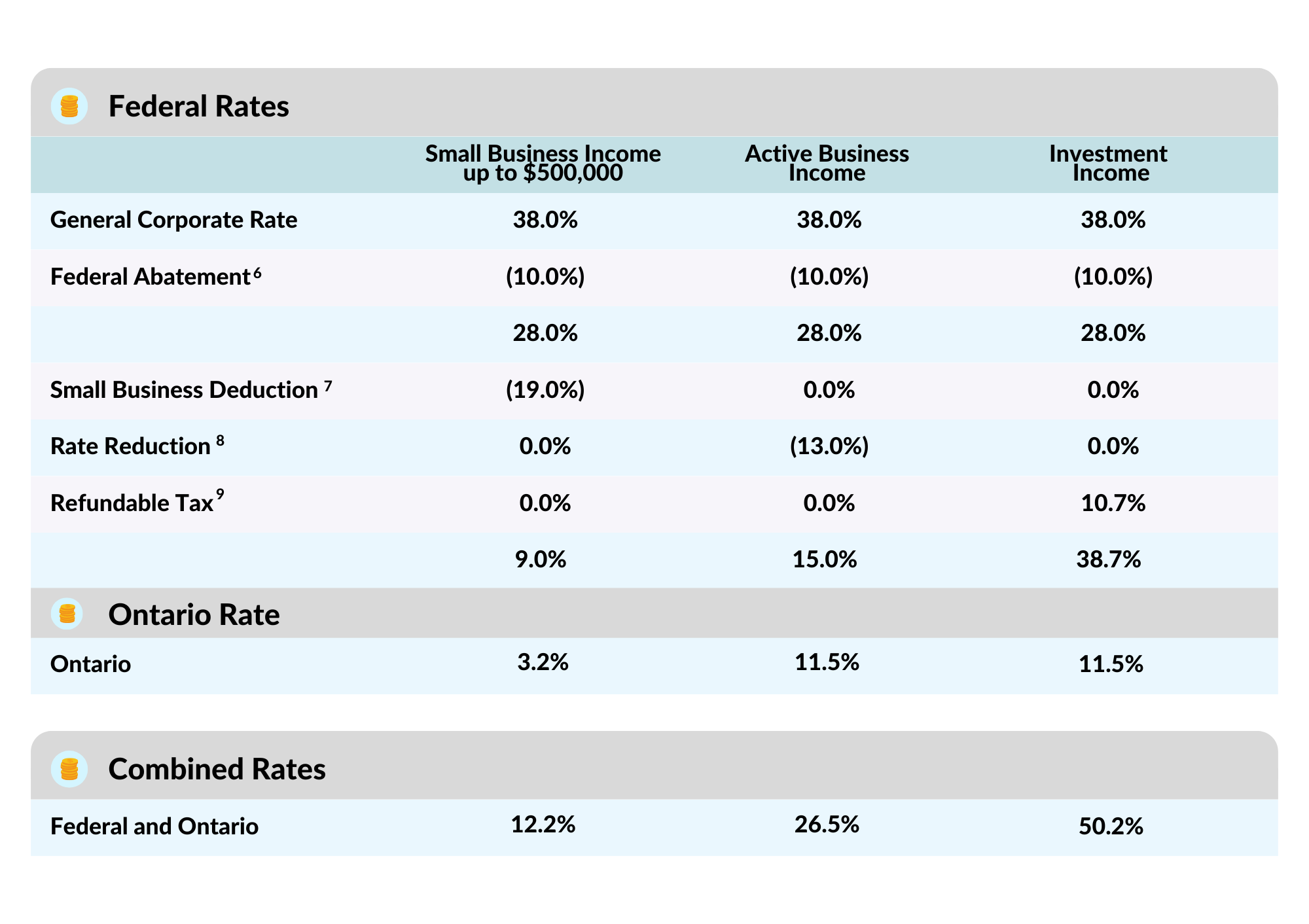

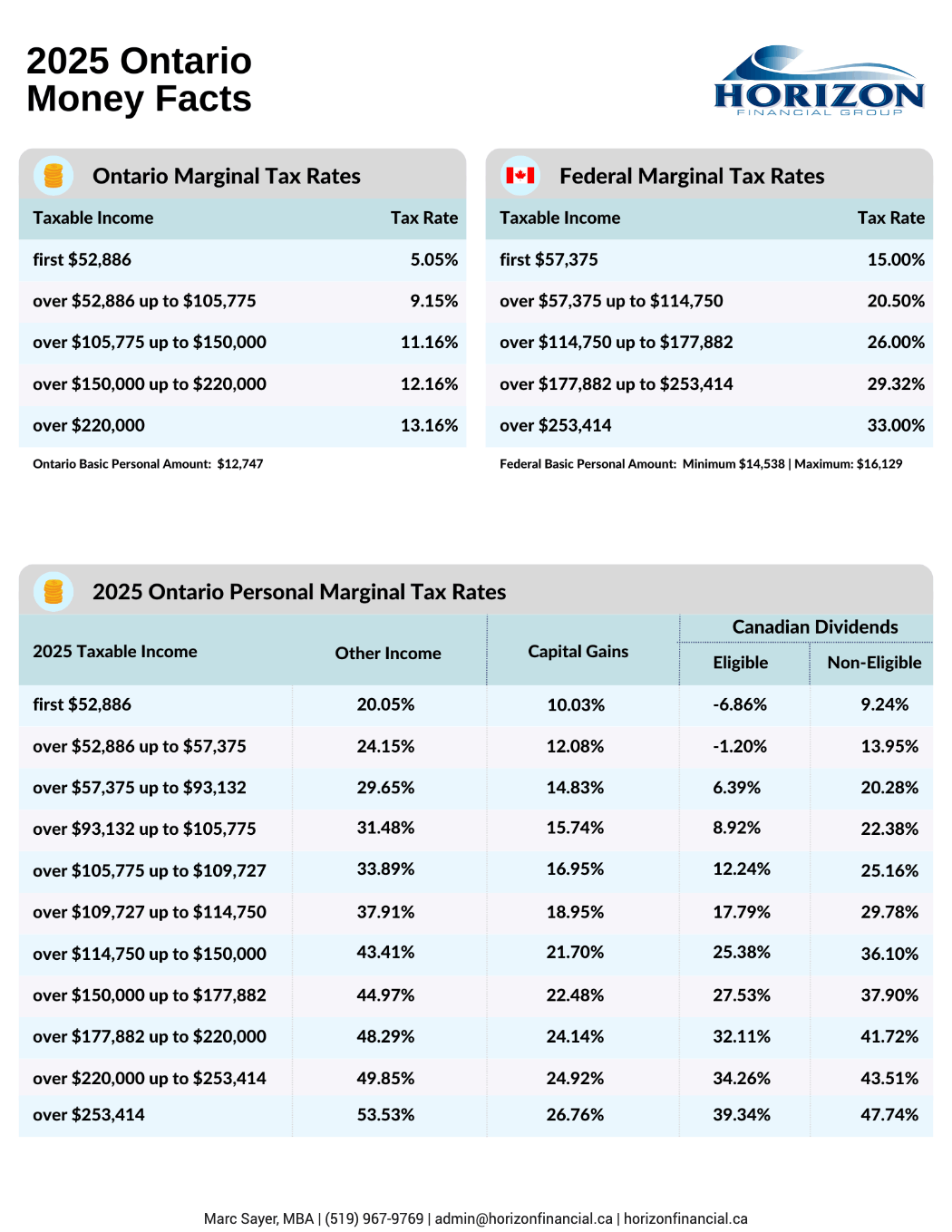









-Marc-Sayer-mcRRGELp35qWo7yqd.png)
-Marc-Sayer-mcRRGELp35qWo7yqd.png)